Guide for COM Team Members
Table of Contents
Introduction and Fundamentals
The main objective is to establish efficient and effective link between the space and the ground segment
- Provide a link to relay data findings (satellite to ground station) and send commands to the satellite
- Provide the interface between the satellite and ground systems
- Receives and demodulates uplink signals and modulates and transmits downlink signals
- Consist of a transmitter, a receiver, an antenna, and a RF coax cable.
-
Relay Payload mission data, and House keeping data
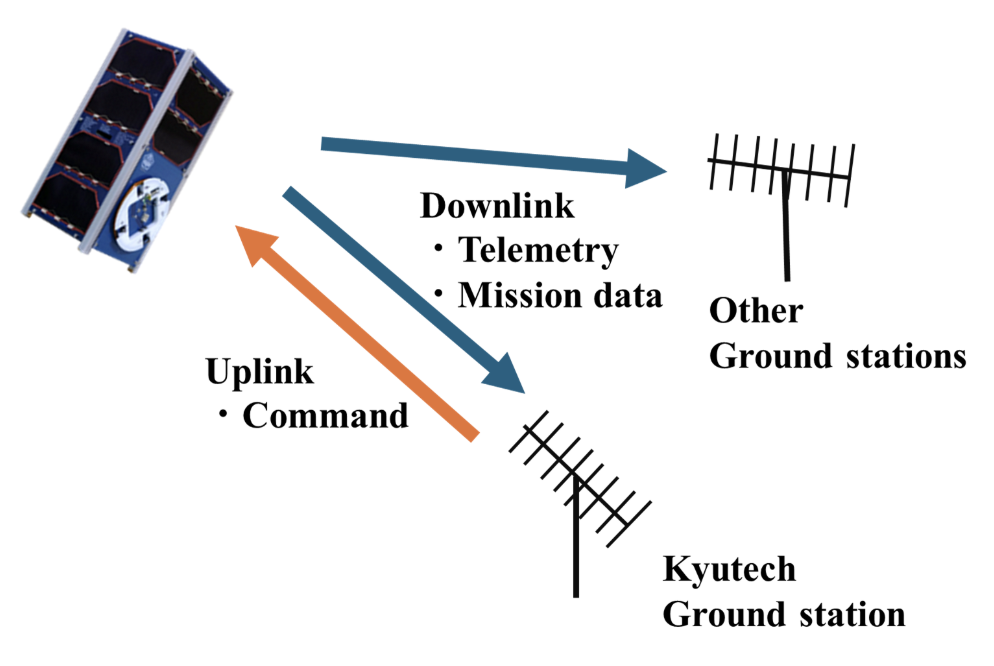
Reference: BirdsX MDR
Overview of RF communication in CubeSats.
Radio Frequency (RF) communication is the backbone of CubeSat operations, enabling critical data exchange between the satellite and ground stations. A reliable RF communication subsystem ensures the successful transmission of telemetry, scientific data, and commands. RF communication involves the use of electromagnetic waves to transmit and receive data. In CubeSats, it typically includes:
- Uplink: Transmission of commands and instructions from the ground station to the CubeSat.
- Downlink: Sending telemetry and payload data from the CubeSat to the ground station.
- Inter-Satellite Links (Optional): Communication between CubeSats in a constellation or swarm.
CubeSats operate within specific frequency bands allocated by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU):
| VHF (Very High Frequency) | UHF (Ultra High Frequency) | S-Band | X-Band | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Range | 30–300 MHz | 300 MHz–3 GHz (commonly 400-450 MHz for CubeSats) | 2–4 GHz (commonly around 2.2-2.3 GHz for CubeSats) | 8–12 GHz |
| Use | Low data rates, mainly for telemetry and beacon signals | Telemetry, command, and low-to-moderate data transfer | High-speed data downlinks, particularly for payload data | High-speed data downlink for advanced CubeSat missions |
| Advantages | Long range and low power requirements | Compact antennas and better penetration through atmospheric layers | High data rates | Extremely high data rates |
| Disadvantages | Larger antennas needed | Limited data rates compared to higher frequencies | Higher power consumption and complex antenna designs | Requires precision antennas and significant power |
The setup consists of
- uplink
- a microcontroller used for communications labelled ‘COM PIC’ - a PIC18F67J94 located on the OBC board
- The COM board inteself containing the Addnics UHF ADD1397D2 tranciever,
- UHF Rx antenna,
- GMSK Demodulator
- downlink
- GMSK/CW modulator
- UHF transmitter
- UHF Tx antenna
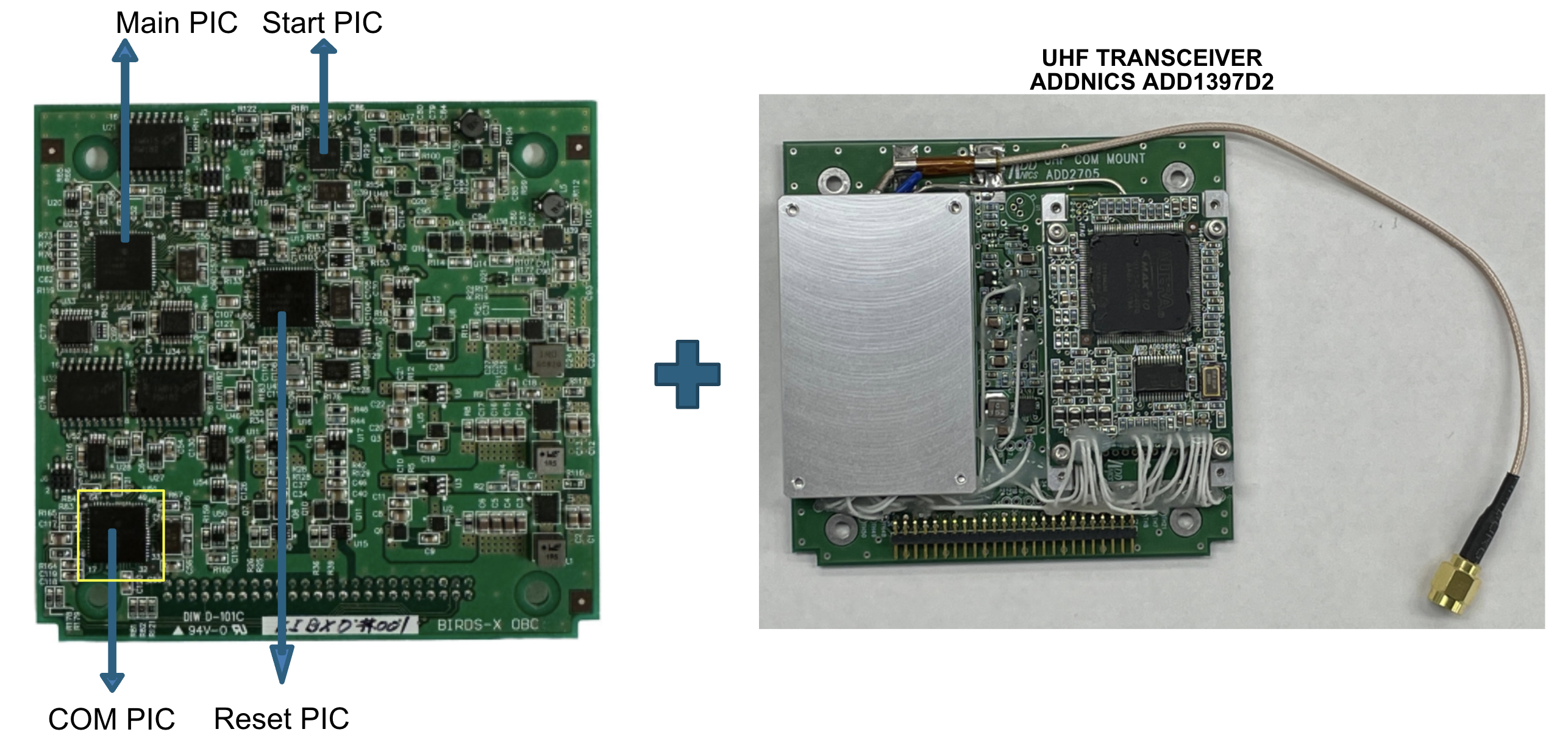
Reference: BirdsX MDR
Evolution of communication systems in these projects
The BIRDS project CubeSats demonstrated robust RF communication using UHF for telemetry and beacon signals, S-Band for high-speed data downlink, and deployable monopole and dipole antennas for effective range and performance. Birds5 had 5 connections to the ADDNICS tranciever but the new com only has 3, 2 UART lines and one DIO enable line
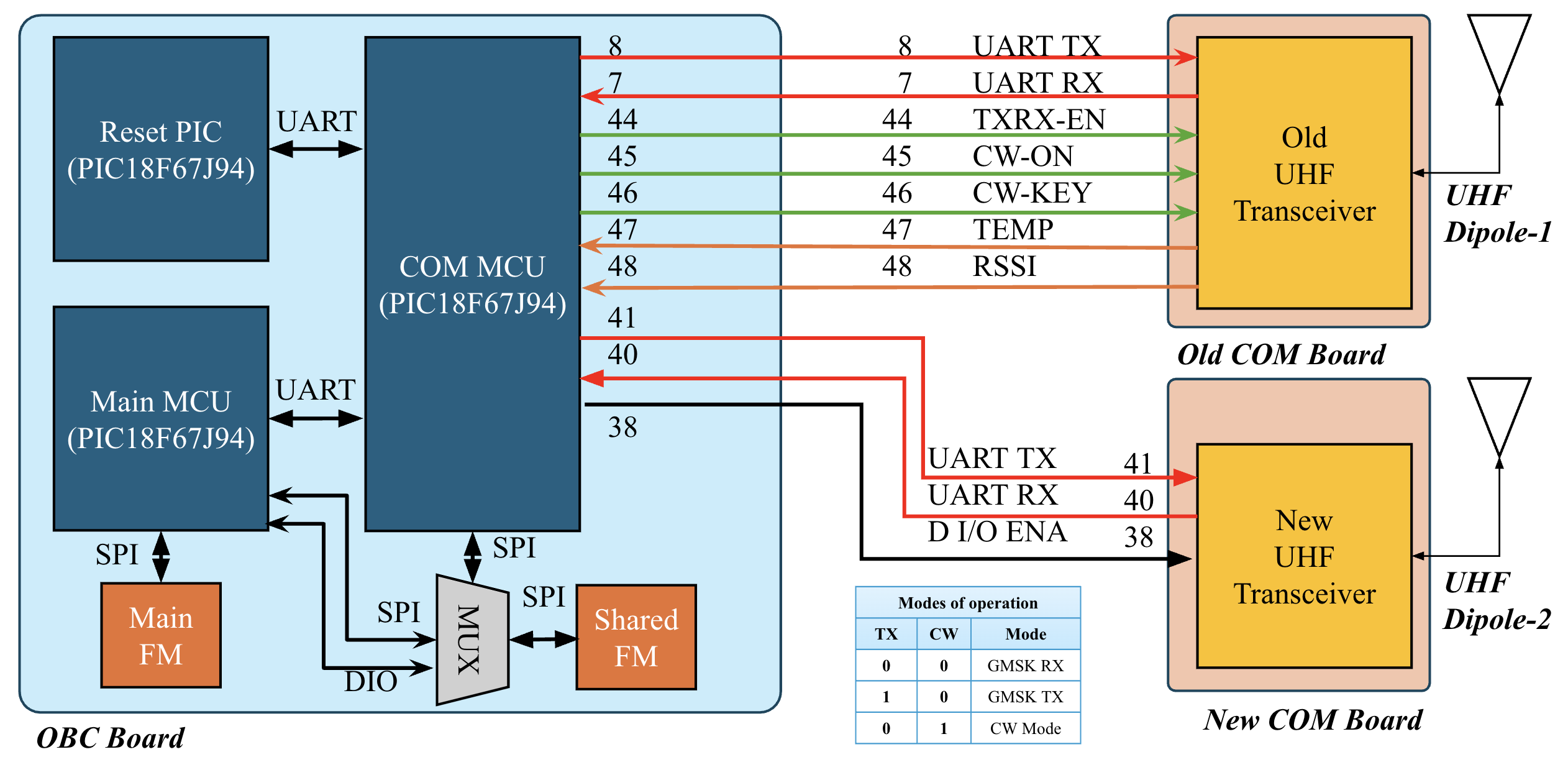
Reference: BirdsX COM block diagram
Role and Responsibilities of the COM Team
Any satellite developer needs to be able to read schematics
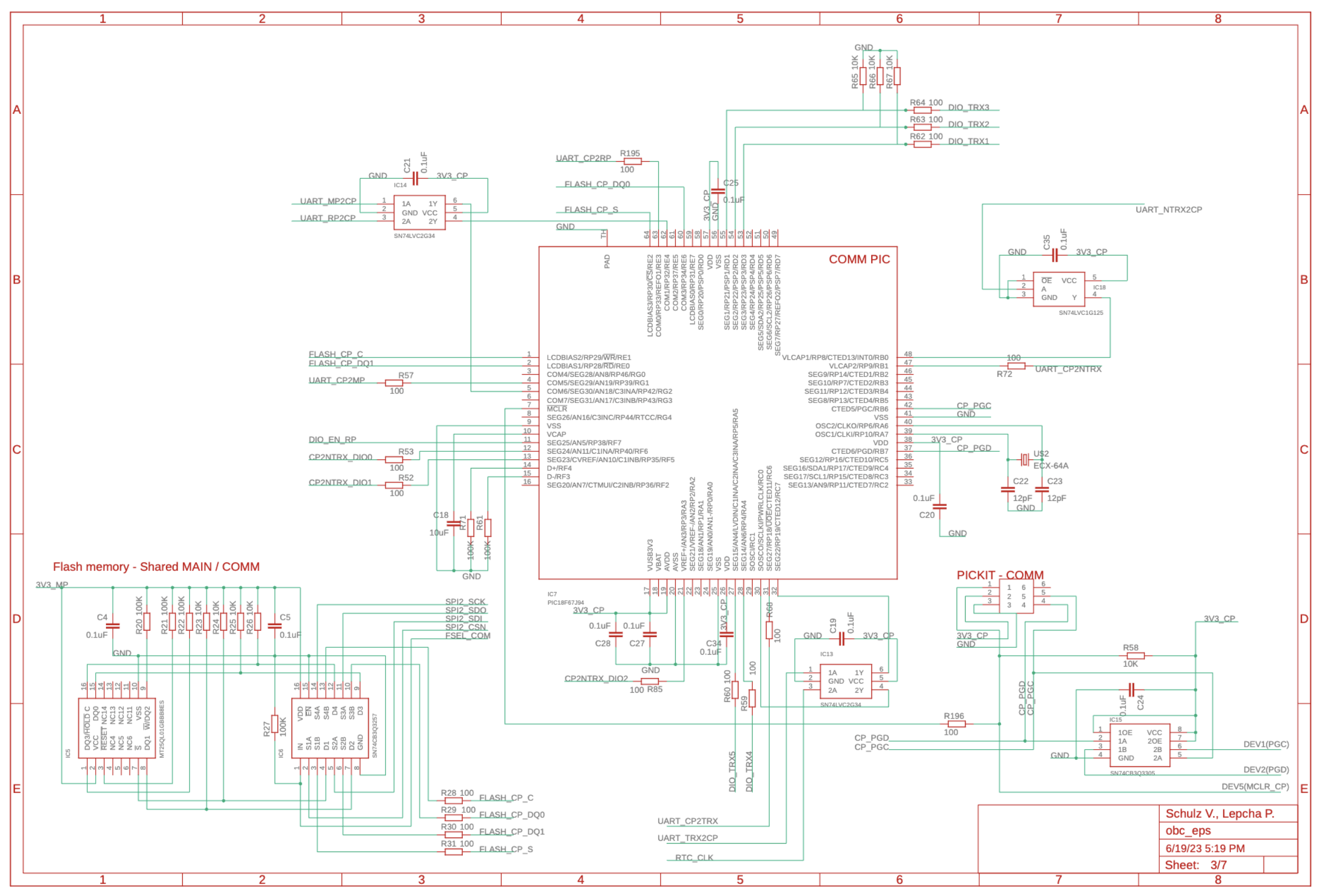
Reference: BirdsX OBC/EPS schematic
Satellite Communication Basics
COM Radio Links
| Uplink (Receive Mode) | Downlink (Transmit Mode) | Beacon (CW Mode) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency | 435.313 MHz | 437.375 MHz | 437.375 MHz |
| Bandwidth | 8.5 kHz | 8.5 kHz | 500 Hz |
| Modulation | GMSK | GMSK | CW Morse Code |
| Output Power | – | 800mW (29.03 dBm) | 100mW (20 dBm) |
| Rate | 4800 bps | 4800 bps | 20 wpm |
Tools and Resources for COM Teams
- Recent Innovations in CubeSat RF Communication Software-Defined Radios (SDRs): Enable reconfigurable communication protocols and frequencies. Phased Array Antennas: Offer dynamic beam steering for improved communication efficiency. Inter-Satellite Communication: Expanding capabilities for CubeSat constellations and swarm missions.
- RF Communication in BIRDS Missions The BIRDS project CubeSats demonstrated robust RF communication using:
UHF for telemetry and beacon signals. S-Band for high-speed data downlink. Deployable monopole antennas for effective range and performance.
Reference Types Technical References:
Block diagrams and system schematics from BIRDS-X, 5, and 4. Datasheets of RF components, transceivers, and antennas used. Simulation results and link budget calculations. Standards and Guidelines:
ITU frequency allocation charts. CCSDS protocols and CubeSat standards. Amateur radio guidelines for CubeSats. Project-Specific Documentation:
BIRDS-X, BIRDS-5, and BIRDS-4 technical papers. Design reviews, subsystem descriptions, and testing reports. Software Tools and Libraries:
Open-source libraries for RF communication (e.g., GNU Radio). Tools for link budget calculations and RF simulations. Case Studies and Mission Reports:
Published papers on BIRDS project achievements and challenges. Lessons learned from CubeSat missions with communication issues. Tutorials and Online Resources:
BIRDS project repositories and wikis. Tutorials on antenna design, RF testing, and ground station setup.